measures of position for ungrouped data|3.E: Measures of Position (Optional Exercises) : iloilo THE MEASURE OF POSITION PERCENTILE RANK STEP 2.B: . All times displayed in Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST is UTC+10) unless stated otherwise. Mater Foundation is registered as a charity with the Australian Charities and Not-for-profits Commission.
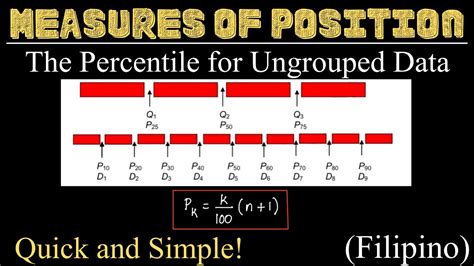
measures of position for ungrouped data,Learn how to calculate and interpret quartiles, deciles, and percentiles for ungrouped data. This presentation covers the definitions, formulas, examples, and applications of these measures of position.5. PROCEDURE 1. Arrange the scores in INCREASING or DECREASING order 2. .

THE MEASURE OF POSITION PERCENTILE RANK STEP 2.B: .
Learn how to illustrate, calculate, interpret, and solve problems involving quartiles, deciles, and percentiles of ungrouped data. This self-learning module contains . MEASURES OF POSITION FOR UNGROUPED DATA - YouTube. WOW MATH. 677K subscribers. Subscribed. 3.5K. 241K views 2 years ago GRADE 10 || FIRST TO FOURTH . It may or may not be part of the data. \(i =\) the index (ranking or position of a data value) \(n =\) the total number of data; Order the data from smallest to largest. .Learn how to calculate percentiles, quartiles, and five-number summary for ungrouped data. See examples, definitions, and formulas for finding these measures of position. Measures of Position (Ungrouped Data) | Basic Statistics - YouTube. Pinoy Mathematician. 12.1K subscribers. Subscribed. 2K. 142K views 3 years ago PHILIPPINES. The .3.E: Measures of Position (Optional Exercises) Quartiles of Ungrouped Data - Measures of Position @MathTeacherGon - YouTube. MATH TEACHER GON. 448K subscribers. 2.3K. 160K views 2 years ago STATISTICS. .
measures of position for ungrouped data 3.E: Measures of Position (Optional Exercises)Measures of Position: Percentiles, Quartiles, Standard Scores. Statisticians often talk about the position of a value, relative to other values in a set of quantitative data. The .Learn how to calculate and interpret the median, quartiles, percentiles, and interquartile range for ungrouped data. See examples, definitions, and formulas for these measures .
Answer. For runners in a race it is more desirable to have a high percentile for speed. A high percentile means a higher speed which is faster. 40% of runners ran at .To find the median, add the two values together and divide by two. 6.8 + 7.2 2 = 7 (2.5.1) (2.5.1) 6.8 + 7.2 2 = 7. The median is seven. Half of the values are smaller than seven and half of the values are larger than seven. Quartiles are .Percentiles. Assume that the elements in a data set are rank ordered from the smallest to the largest. The values that divide a rank-ordered set of elements into 100 equal parts are called percentiles. An element having a percentile rank of P i would have a greater value than i percent of all the elements in the set. Thus, the observation at the 50th percentile . Measures of Position for Ungroup Data. This document discusses measures of central tendency and dispersion for ungrouped data, including the mean, quartiles, deciles, and percentiles. It provides formulas for calculating these values and examples worked out step-by-step. The mean is defined as the average value of the data.

In this video, you will learn about the measures of position for ungrouped data using general method. @MathTeacherGon will discuss the concept behind quartiles of ungrouped data. He will also intruduce you to the different formula in calculating for the quart. MATHEMATICS Quarter 4 – Module 6 Measures of Position and Other Statistical Methods; MATHEMATICS Quarter 4 – Module 5 Statistical Mini-Research; MATHEMATICS Quarter 4 – Module 2 Calculating Measures of Position for Grouped Data; MATHEMATICS Quarter 4 – Module 3 Interpreting Measures of Position
The common measures of location are quartiles and percentiles.. Quartiles are special percentiles. The first quartile, Q 1, is the same as the 25 th percentile, and the third quartile, Q 3, is the same as the 75 th percentile. The median, M, is called both the second quartile and the 50 th percentile. To calculate quartiles and percentiles, you must order the data .
Illustrate the following measure of position in ungrouped data: percentile, decile, and quartile. b. Calculate a specified measure of position of a set ungrouped data. c. Interpret measures of position. d. Solve problems involving measures of position. II.(KNOWLEDGE): 1. determine the quartiles of an ungrouped data (SKILLS): 2. solve quartile value of an ungrouped data (ATTITUDE): 3. appreciate the concept of measures of position in real lifeAnother measure of position is the quartile, which is similar to the percentile except that it divides data into quarters (segments of 25% each) instead of hundredths. Thus, the n th quartile is the value x for which (25 n )% of the values are less than or equal to x. Three quartiles are defined: Q1, Q2, and Q3.
A group of students obtained the following scores in Statistics quiz: 8, 2, 5, 4, 8, 5, 7, 1, 3, 6 GROUP ACTIVITY. 5. PROCEDURE 1. Arrange the scores in INCREASING or DECREASING . Understanding the measures of central tendencies of ungrouped data. (i) MODE: The most frequently occurring item/value in a data set is called mode. Bimodal is used in the case when there is a tie .measures of position for ungrouped dataAnother measure of position is the quartile, which is similar to the percentile except that it divides data into quarters (segments of 25% each) instead of hundredths. Thus, the n th quartile is the value x for which (25 n )% of the values are less than or equal to x. Three quartiles are defined: Q1, Q2, and Q3.¥ÿ 1 @òñ : cÜÐ ¿þüûý„›þÌøª7 ú"ºŸZ°ŠÃLR8¬iòGnââ pNòÉÏà‚ðÀ j Z Ÿ `žqœ¾øôÝÔõõDO_D\ôtO^ôt_×ýòø™š¨ €s®×«ÇG Mé³ i¶ mgÀPÄÀaÝè% – ÕàÌ pŒ¢ 9x % õ -*5Y%h†bFXÖ r4&‚ö l¼%XŠ nÓ µz4 ¦ ¸ $?ìYDÓ . 1Ô=«/ € d&"6( “ ®vÄã% ÁŠ ¯ˆ¼ * IºÔ ŽfŠ C¶9Í¢xD[Qó yjQ H-kÈvÕ9'fú½˜4 § |¸ Ѧ®’º . StatisticsQuartiles, Deciles, and Percentiles for Ungrouped Data | Measures of Position | Statistics Measures of Position. Statisticians often talk about th.A. Topic: Measures of Position: The Quartiles for Ungrouped Data B. References: Book: . Measures of Position has two types of data the Ungrouped Data and Grouped Data. ut for today’s lesson we .
Illustrating The Measures of Position for Ungrouped Data. Mathematics – Grade 10 Alternative Delivery Mode Quarter 4 – Module 1: Illustrating the following Measures of Position for Ungrouped Data First Edition, 2020. Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines . For Online, Blended, and Modular students, please take time to watch the video before answering the Google forms given by your teacher related to the lesson..
measures of position for ungrouped data|3.E: Measures of Position (Optional Exercises)
PH0 · Quartiles of Ungrouped Data
PH1 · Measures of Position: Percentiles, Quartiles, Standard Scores
PH2 · Measures of Position (Ungrouped Data)
PH3 · MEASURES OF POSITION FOR UNGROUPED DATA
PH4 · Grade 10 Mathematics Module: Measures of Position of Ungrouped Data
PH5 · Grade 10 Mathematics Module: Measures of Position of
PH6 · 3.E: Measures of Position (Optional Exercises)
PH7 · 3.3: Measures of Position
PH8 · 2.3 Measures of the Location of the Data
PH9 · 1.5.2